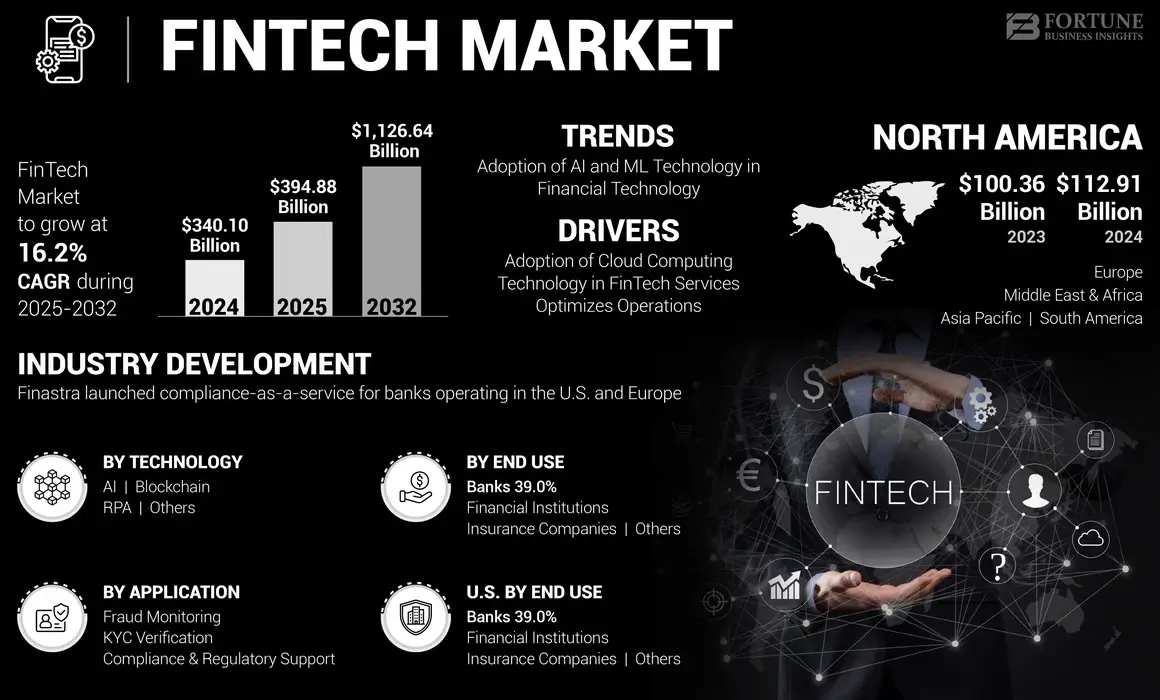
With the continuous improvement of global data privacy protection awareness and increasingly strict regulatory environment, data localization has become an important challenge for fintech companies expanding globally. This article provides an in-depth analysis of global data localization trends and data localization strategies for fintech enterprises, helping enterprises operate in compliance.
1. Global Data Localization Trends
Data localization refers to legal or regulatory requirements that mandate data storage and processing in specific geographic locations. In recent years, global data localization trends have become increasingly evident, and more and more countries and regions have introduced data localization-related laws and regulations.
| Region/Country | Data Localization Requirements | Effective Date |
|---|---|---|
| European Union | General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) allows cross-border data transfers but requires specific conditions | May 2018 |
| China | Operators of critical information infrastructure must store personal information and important data within the country | September 2021 |
| India | Sensitive personal data must be stored locally, non-sensitive data can be transferred cross-border | August 2023 |
| Indonesia | Electronic system operators must store data related to public services locally | September 2020 |
| Russia | Personal data of Russian citizens must be stored locally | September 2015 |
| Brazil | Personal data can be transferred cross-border but requires specific conditions | September 2020 |
| Vietnam | Specific types of data must be stored locally | January 2023 |
According to relevant reports, more than 100 countries and regions around the world have introduced data localization-related laws and regulations, covering multiple industries such as finance, healthcare, and telecommunications.
2. Driving Factors for Data Localization
2.1 Data Security and Sovereignty
Data has become an important strategic resource for countries, and governments are paying more and more attention to data security and sovereignty. Through data localization requirements, governments can better protect national data security and sovereignty, and prevent sensitive data from being obtained and abused by foreign forces.
2.2 Data Privacy Protection
With the continuous improvement of data privacy protection awareness, governments around the world have introduced data privacy protection-related laws and regulations, such as the EU's GDPR and China's Personal Information Protection Law. Data localization is one of the important means to achieve data privacy protection.
2.3 Regulatory Law Enforcement Needs
Data localization can make it easier for regulatory authorities to access and obtain data, facilitating regulatory law enforcement. For key regulatory areas such as the financial industry, data localization requirements are particularly strict.
2.4 Economic Development Considerations
Data localization can promote the development of local data centers and cloud computing industries, create employment opportunities, and drive digital economic development.
3. Challenges Faced by Fintech Enterprises in Data Localization
3.1 Increased Compliance Costs
Data localization requires enterprises to establish local data centers or use local cloud service providers in target markets, which will significantly increase enterprises' IT infrastructure costs and operational costs.
3.2 Complex Technical Architecture
Data localization requires enterprises to redesign and adjust their technical architecture to achieve local data storage and processing, which will increase the complexity and maintenance costs of the technical architecture.
3.3 Restrictions on Cross-Border Data Transfers
Data localization is usually accompanied by restrictions on cross-border data transfers, which will affect the global operation and data sharing of enterprises, increasing the difficulty of business operations.
3.4 Inconsistent Regulatory Requirements
Data localization requirements vary across countries and regions, which brings challenges to the cross-border operations of fintech enterprises. Enterprises need to understand the data localization requirements of each target market and formulate corresponding compliance strategies.
4. Data Localization Strategies for Fintech Enterprises
4.1 Conduct Advance Compliance Assessment
Before entering the target market, enterprises need to conduct advance data localization compliance assessments to understand local data localization requirements and regulatory trends, including:
- What types of data need to be stored locally
- Specific requirements and timelines for data localization
- Conditions and restrictions for cross-border data transfers
- Legal consequences for violating data localization requirements
4.2 Choose the Appropriate Data Storage Solution
Choose the appropriate data storage solution based on the data localization requirements of the target market and the enterprise's business needs:
Local Data Center
Establish or lease a local data center in the target market to fully control data storage and processing.
Advantages: Fully comply with data localization requirements, high data control.
Disadvantages: High initial investment, high operating costs, low flexibility.
Local Cloud Services
Use local cloud service providers in the target market, such as AWS, Azure, and Alibaba Cloud data centers in local regions.
Advantages: Low initial investment, high flexibility, strong scalability.
Disadvantages: Relatively low data control, dependency on cloud service providers.
4.3 Optimize Data Architecture Design
According to data localization requirements, optimize data architecture design to achieve local data storage and processing:
- Data classification and grading: Classify and grade data according to its sensitivity and importance, and determine which data needs to be stored locally.
- Distributed architecture: Adopt a distributed architecture to store data in different geographic locations, meeting data localization requirements of different markets.
- Data synchronization mechanism: Establish an efficient data synchronization mechanism to ensure data consistency and integrity in different geographic locations.
- Privacy computing technology: Adopt privacy computing technologies, such as federated learning and multi-party secure computing, to conduct data analysis and processing without sharing raw data.
4.4 Establish a Data Compliance Management System
Establish a comprehensive data compliance management system to ensure the effective implementation of data localization requirements:
- Develop data compliance policies: Formulate comprehensive data compliance policies and processes, clarifying data localization requirements and implementation steps.
- Establish a data compliance team: Establish a dedicated data compliance team responsible for the implementation and management of data localization.
- Implement data compliance training: Regularly conduct data compliance training for employees to improve their data compliance awareness and capabilities.
- Establish a data compliance audit mechanism: Conduct regular data compliance audits to ensure the effective implementation of data localization requirements.
4.5 Actively Participate in Industry and Regulatory Dialogues
Actively participate in industry and regulatory dialogues, understand the latest trends and requirements of data localization, and provide industry opinions and suggestions for the formulation and improvement of regulatory policies.
5. Future Outlook of Data Localization
With the continuous improvement of global data privacy protection awareness and increasingly strict regulatory environment, data localization trends will continue to strengthen. In the future, data localization requirements may become more strict and detailed, involving more industries and data types.
At the same time, with the continuous development of technology, new technologies such as privacy computing and blockchain may provide new solutions for data localization, achieving efficient data sharing and utilization while meeting data localization requirements.
6. Conclusion
Data localization has become an important challenge for fintech companies expanding globally. Enterprises need to fully understand global data localization trends and data localization requirements of target markets, formulate appropriate data localization strategies, including conducting advance compliance assessments, choosing appropriate data storage solutions, optimizing data architecture design, and establishing a data compliance management system.
Through effective data localization strategies, fintech companies can meet regulatory requirements while achieving global business development. With the continuous development of technology and gradual improvement of the regulatory environment, the implementation costs and difficulties of data localization may decrease, creating a better environment for the global development of fintech enterprises.